JZJ-A Foundry Pouring Manipulator Instruction Manual
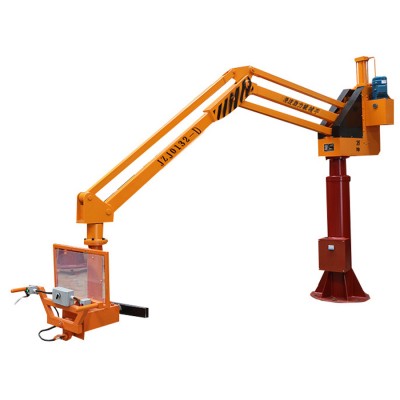
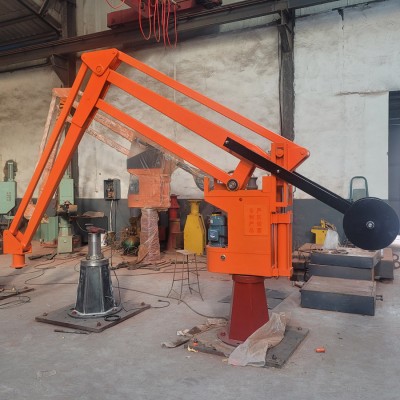
The JZJ-A Foundry Pouring Manipulator consists of six components: a column, an arm base, a rod system, a spreader, a hydraulic power unit, and an electrical control system.
Structural Description
A bearing is installed at the top of the column, which is connected to the arm base, enabling 360° rotation. A hydraulic cylinder is mounted on one side of the arm base, and the end of the hydraulic cylinder piston rod is connected to the rod system. The other end of the rod system is equipped with a spreader, and the clamping end of the spreader is fitted with a ladle. The spreader includes a vertically arranged vertical rod, with a horizontal sleeve installed at the lower end of the vertical rod, and a ladle fixing device mounted at one end of the sleeve. When the power unit operates, the piston rod drives the rod system to lift up and down, thereby raising and lowering the ladle.
A rod system traveling bearing is placed on the top of the arm base. The traveling bearing moves back and forth on the top of the arm base, causing several joints of the rod system to fold and telescope simultaneously, thus driving the ladle to move forward and backward.
Why can the ladle remain balanced at any point in the plane when empty or loaded, i.e., neutral equilibrium in mechanics? This is precisely because the designer skillfully applied the principle of equilibrium in mechanics in the rod system design. The four-bar linkage achieves automatic balance through a parallelogram design, and the geometric relationship between the counterweight and the boom is fixed, enabling natural maintenance of torque balance during movement.
Static Balance Design: The weight and position of the counterweight are accurately calculated based on the rod system length and load range during initial design, ensuring the ladle remains balanced at different horizontal positions.
The spreader is connected to the end of the rod system via a bearing. A horizontal sleeve is installed at the lower end of the vertical rod, and a rotating shaft is connected inside the sleeve through a bearing. A ladle fixing device is mounted at one end of the rotating shaft.
This machine does not require travel switches; it utilizes the inherent stroke limit of hydraulic actuators and is equipped with a buffer device. The piston rod's vertical movement drives the boom to lift and lower, ensuring smooth operation. A safety device is installed in the hydraulic system to provide protection against overloads, preventing damage to mechanical components and accidents.
Rotation control points are set during the pouring process. Manual auxiliary tilting is achieved through a manual release device handbrake engaged by pins and gears.
The top of the vertical rod is rotatably connected to the end of the rod system via a bearing, allowing the spreader to rotate flexibly within a 360° range to adapt to different pouring angles and position requirements. Meanwhile, the brake handle on the grip is connected to the brake disc inside the sleeve via a brake cable. Operators can pull the brake handle to fix the ladle with the brake disc as needed, ensuring the stability of the spreader during pouring. This dual fixing mechanism effectively prevents loosening, deviation, and other issues of the ladle during pouring, guarantees pouring accuracy and consistency, and improves casting quality.
The protective baffle provides additional safety for operators. During pouring, it can block splashing high-temperature molten metal, avoiding harm to operators.
Figure Description
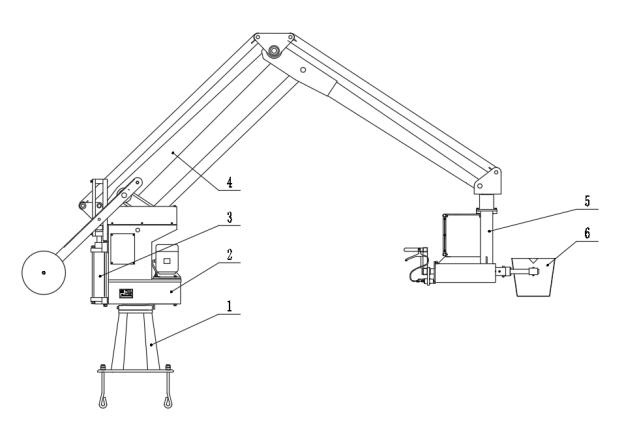

1.Column; 2. Arm base; 3. Hydraulic cylinder; 4. Rod system; 5. Spreader; 51. Vertical rod; 52. Protective baffle; 53. Sleeve; 54. Bracket; 541. Grip; 55. Brake handle; 56. Ladle fixing device; 561. Washer; 562. Connecting rod; 6. Ladle.
Equipment Performance Features
1.No travel switches required; stroke limitation is achieved through the inherent stroke of the oil cylinder. The piston rod's vertical movement drives the boom to lift and lower, and a buffer device is equipped for smooth operation with minimal impact.
2.A safety device is installed in the hydraulic system to provide protection against overloads, avoiding damage to mechanical transmission components and safety accidents.
3.Using hydraulic oil as the working medium, the hydraulic transmission device can self-lubricate, resulting in low wear, low noise, and a long service life.
4.For lifting the same weight, the motor power of hydraulic transmission is 0.3-0.5 times that of mechanical transmission, achieving energy conservation and consumption reduction.
5.The product has low later maintenance costs, requiring only replacement of damaged seals.
6.The column and main components of this product are made of cast steel and steel plate welded structures, greatly improving overall rigidity and strength, and eliminating potential safety hazards.
7.The hydraulic valve closes after power failure to prevent the ladle from falling. It operates smoothly with stable and reliable braking, no jitter or sliding.
8.All materials used comply with national standards and specifications.
9.Complete protection functions, including overtravel protection, overload protection, and short-circuit or overload protection for electrical loads.
10.All electrical components and materials are 3C-certified products (China Compulsory Certification).
Safety Precautions
1.A three-phase leakage protection switch should be installed before connecting the power supply to the machine.
2.The machine shell must be grounded (PE wire) with good grounding.
3.Before opening the electrical box cover for maintenance, the external power supply must be cut off first.
4.Rainproof and dustproof measures should be taken during outdoor operation. It is strictly prohibited for rainwater to wet electrical appliances or enter the oil tank.
5.The battery of the remote control transmitter should be replaced every two months (depending on usage).
6.Regularly check whether the bolts at each connection part are loose.
7.Regularly inspect electrical appliances for looseness.
8.Hydraulic oil should be cleaned and replaced quarterly depending on usage.
9.Calcium-based grease is used for lubricating the rolling bearings at various parts of the machine, which should be cleaned and replaced every six months.
10.The contact surface between the front and rear vertical guide rails and the rollers is lubricated with calcium-based grease, which should be lubricated monthly.
11.32#~48# anti-wear hydraulic oil is used in the oil tank, and the oil level should not be lower than 10mm below the oil level line of the oil sight glass. The hydraulic oil model is determined according to the operating environment, and it should be cleaned and replaced every six months.
Wear Parts List
- Positioning handbrake and brake cable
- Switch buttons





